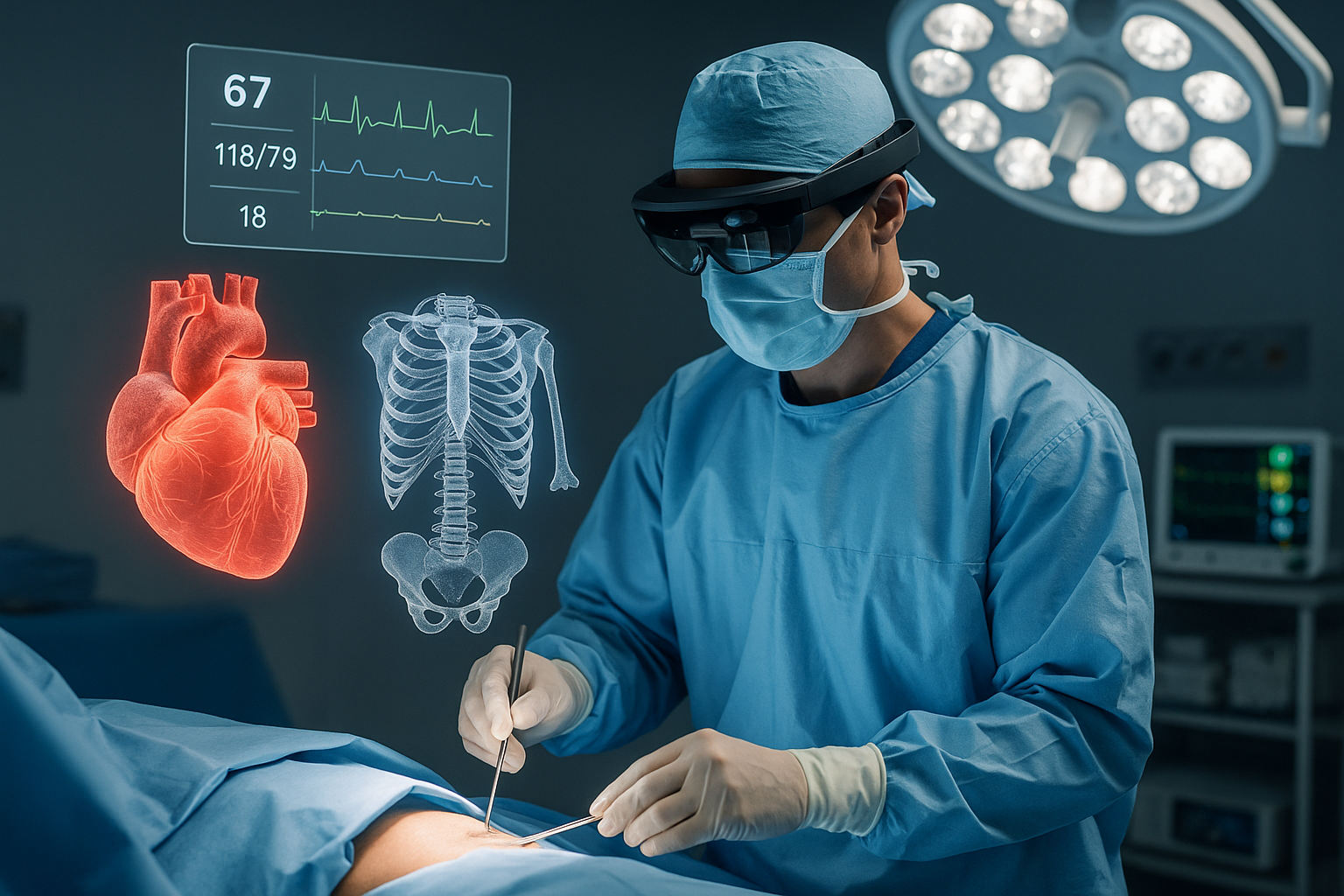
What’s new in AR this month? In August 2025, Johns Hopkins Hospital announced its expansion of AR-assisted surgeries, reporting improved accuracy in orthopedic procedures. Meanwhile, Philips launched an AR imaging tool that overlays CT and MRI scans onto patients during surgery, giving doctors a real-time roadmap inside the operating room. These innovations highlight the growing role of augmented reality (AR) in modern healthcare, blending precision, efficiency, and immersive visualization.
Why AR in Healthcare Matters
Healthcare is a field where precision, speed, and training directly affect lives. Traditional methods often involve static images, delayed data, and manual training models. AR bridges these limitations by providing real-time, interactive, 3D insights for both practitioners and patients. From improving diagnostic accuracy to transforming medical education, AR is becoming one of the most valuable tools in the healthcare ecosystem.
Core Applications of AR in Healthcare
1. Surgical Assistance
Surgeons can wear AR headsets that project 3D overlays of patient anatomy during operations. For example, an orthopedic surgeon sees a holographic map of a patient’s bones, blood vessels, or nerves, reducing risks and improving precision. AR also reduces surgery time by eliminating the need to switch between live patients and 2D imaging screens.
2. Diagnostics and Imaging
Radiologists and clinicians use AR to overlay diagnostic scans onto physical patients. Instead of analyzing CT or MRI scans in isolation, doctors can “see through” the body with aligned AR visuals. This contextualizes medical data and makes diagnosis faster and more accurate.
3. Medical Training
AR is transforming how medical students and professionals learn. Anatomy lessons, once limited to cadavers, now feature AR overlays that allow exploration of organs, blood flow, and cellular activity. Surgical trainees can practice procedures in risk-free AR simulations, preparing them for real-world challenges.
4. Patient Education and Care
Doctors use AR to explain diagnoses and treatment options to patients. For example, cardiologists project a 3D beating heart to illustrate blocked arteries. Physical therapists employ AR games that guide patients through rehabilitation exercises, turning recovery into an engaging process.
5. Remote Collaboration
With AR, surgeons and specialists across the globe can collaborate in real time. Using shared AR platforms, experts annotate live visuals and guide procedures remotely, improving access to specialized care in underserved regions.
Real-World Case Studies
- Johns Hopkins Hospital: Expanded AR in orthopedic surgeries, improving alignment accuracy by 19%.
- Philips AR Imaging: New surgical imaging platform overlays scans directly on patients, reducing surgery time by 25%.
- Stanford Medical School: Students train with AR-enabled anatomy visualizations, improving exam performance by 20%.
- Remote Surgery in India: Surgeons collaborated with U.S. specialists via AR headsets, performing complex procedures with higher success rates.
Quick Facts & Data Insights
- AR in healthcare is projected to be a $10.5 billion industry by 2030.
- AR-assisted surgeries reduce complication risks by up to 17%.
- Medical students using AR training retain 30% more knowledge compared to traditional methods.
Benefits of AR in Healthcare
- Precision: Real-time overlays improve surgical and diagnostic accuracy.
- Efficiency: Faster operations and diagnoses save costs and resources.
- Education: Medical training becomes more engaging, effective, and scalable.
- Patient engagement: Patients understand treatments better with 3D visualizations.
Challenges to Adoption
- Hardware limitations: AR glasses for medical use are still bulky and expensive.
- Integration: AR must sync with hospital IT, imaging, and patient record systems.
- Privacy and security: Handling sensitive medical data in AR requires strict safeguards.
- Regulation: Healthcare AR tools must pass rigorous approvals before clinical use.
Best Practices for AR in Healthcare
- Start with specialized use cases: Focus on high-impact areas like surgery or imaging before scaling.
- Train staff: Provide onboarding and continuous education for surgeons, nurses, and students.
- Integrate with digital twins: Pair AR overlays with patient-specific 3D models for personalized care.
- Ensure compliance: Adopt HIPAA- and GDPR-compliant AR platforms to protect patient data.
Looking Ahead: AR in Healthcare by 2030
By 2030, AR will be a standard part of clinical practice. Surgeons will rely on AR overlays as much as traditional imaging, while patients will expect AR visualizations as part of their care journey. Medical schools will integrate AR as a core teaching method, replacing much of today’s cadaver-based anatomy. Combined with AI, AR will also enable predictive healthcare, where risks are detected before symptoms appear. In this future, AR will not just support healthcare—it will redefine it.
Key Takeaways
- AR in healthcare bridges diagnostics, surgery, education, and patient care with real-time insights.
- Real-world hospitals and schools already report measurable benefits in accuracy and outcomes.
- Challenges remain in hardware, regulation, and integration, but adoption is accelerating.
- By 2030, AR will be indispensable in hospitals, classrooms, and patient interactions worldwide.